React navigation is one of the go to libraries to help build fluid react-native screens. Its easy to setup and is completely customizable. React-navigation allows you to build different types of navigators like top and bottom tabs, and side drawers. React Navigation 5.0 brings with it many additions to the library, such as dynamic screens and support for the latest react features like hooks.
In this guide, we will walk through how to build an authorization flow for your react-native app.

Assumptions
I wont’ go through basic react-native setup, I’m assuming you have a hello-world app running and want to use react-navigation.
Note: I have ejected expo but this shouldn’t affect you.
Setup
Lets start by installing react-navigation 5.0 core dependencies into your react-native application
npm install react-native-reanimated react-native-gesture-handler react-native-screens react-native-safe-area-context @react-native-community/masked-viewnext we will need to install indicative and react-native-elements
npm i indicative react-native-elementsEnsure your package.json have dependencies below:
"@react-navigation/stack": "5.1.0",
"@react-navigation/drawer": "^5.1.0",
"react-native-elements": "1.2.7",
"indicative": "^7.4.4",Screens
The signUp & signIn screens will use indicative for input validation, and react-native-elements to build the screens.
The screens leverage useContext to get state from the app.js createContext, this will pass data around our application to decide which screen the user should be on.
The screens will need to validate users email format and a password length before being authorized to visit the home screen. This is the job of indicative, here is a snippet of the helper function.
import { validateAll } from 'indicative/validator';
const handleSignUp = () => {
const rules = {
email: 'required|email',
password: 'required|string|min:6|max:40|confirmed'
};
const data = {
email: emailAddress,
password: password,
password_confirmation: passwordConfirm
};
const messages = {
required: field => ${field} is required,
'username.alpha': 'Username contains unallowed characters',
'email.email': 'Please enter a valid email address',
'password.min':
'Password is too short. Must be greater than 6 characters',
'password.confirmed': 'Passwords do not match'
};
validateAll(data, rules, messages)
.then(() => {
console.log('success sign in');
signUp({ emailAddress, password });
})
.catch(err => {
const formatError = {};
err.forEach(err => {
formatError[err.field] = err.message;
});
setSignUpErrors(formatError);
});
};SignUp Screen
The SignUpScreen displays a few input boxes and a button, it will call the helper function handleSignUp() to validate users input once they click the sign up button. If the user intended to visit the Sign In screen, we call the singIn context.
We set useEffect to update the screen when an error occurs.
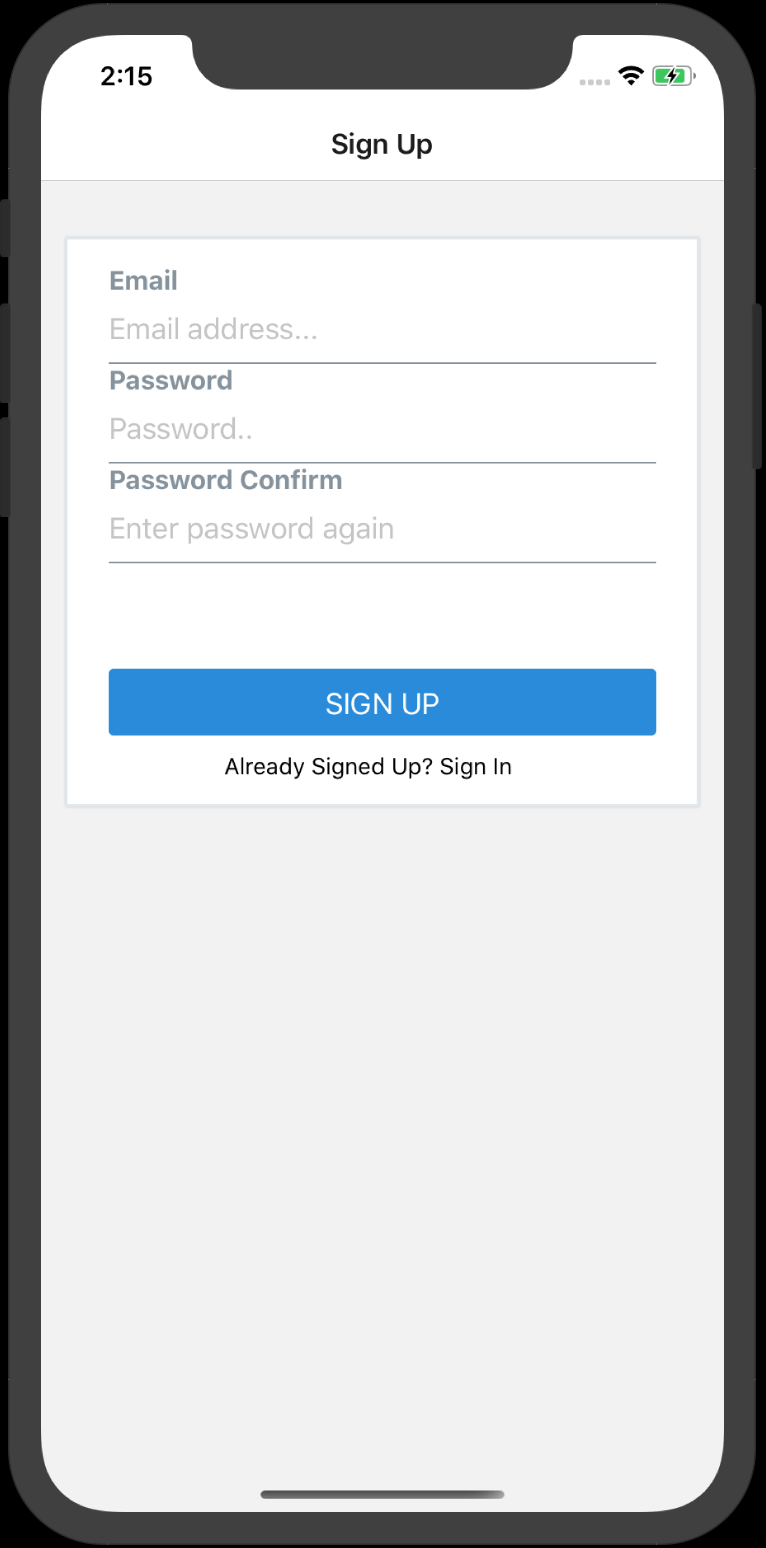
Here is the complete signUpScreen.js,
import React, { useEffect, useState, useContext } from 'react';
import { validateAll } from 'indicative/validator';
import { View, Text } from 'react-native';
import {
Input,
Card,
FormValidationMessage,
Button
} from 'react-native-elements';
import { AuthContext } from '../../../utils/authContext';
const SignUpScreen = ({ navigation }) => {
const [emailAddress, setemailAddress] = useState('');
const [password, setPassword] = useState('');
const [passwordConfirm, setPasswordConfirm] = useState('');
const [SignUpErrors, setSignUpErrors] = useState({});
const { signUp, signIn } = useContext(AuthContext); // should be signUp
const handleSignUp = () => {
// https://indicative.adonisjs.com
const rules = {
email: 'required|email',
password: 'required|string|min:6|max:40|confirmed'
};
const data = {
email: emailAddress,
password: password,
password_confirmation: passwordConfirm
};
const messages = {
required: field => ${field} is required,
'username.alpha': 'Username contains unallowed characters',
'email.email': 'Please enter a valid email address',
'password.min':
'Password is too short. Must be greater than 6 characters',
'password.confirmed': 'Passwords do not match'
};
validateAll(data, rules, messages)
.then(() => {
console.log('success sign in');
signUp({ emailAddress, password });
})
.catch(err => {
const formatError = {};
err.forEach(err => {
formatError[err.field] = err.message;
});
setSignUpErrors(formatError);
});
};
useEffect(() => {}, [SignUpErrors]);
return (
<View style={{ paddingVertical: 20 }}>
<Card>
<Input
label={'Email'}
placeholder="Email address..."
value={emailAddress}
onChangeText={setemailAddress}
errorStyle={{ color: 'red' }}
errorMessage={SignUpErrors ? SignUpErrors.email : null}
/>
<Input
label={'Password'}
placeholder="Password.."
value={password}
onChangeText={setPassword}
secureTextEntry
/>
<Input
label={'Password Confirm'}
placeholder="Enter password again"
value={passwordConfirm}
onChangeText={setPasswordConfirm}
secureTextEntry
/>
<Text style={{ color: 'red', marginLeft: 10, fontSize: 10 }}>
{SignUpErrors ? SignUpErrors.password : null}
</Text>
<Button
buttonStyle={{ margin: 10, marginTop: 50 }}
backgroundColor="#03A9F4"
title="SIGN UP"
onPress={() => handleSignUp()}
/>
<Text style={{ marginLeft: 80 }} onPress={() => signIn()}>
Already Signed Up? Sign In
</Text>
</Card>
</View>
);
};
export default SignUpScreen;SignIn Screen
The signInScreen is very similar, with the difference being the click message the user sees to sign up if they don’t have an account already. We use context to call singUp, sending an empty payload to our reducer in app.js
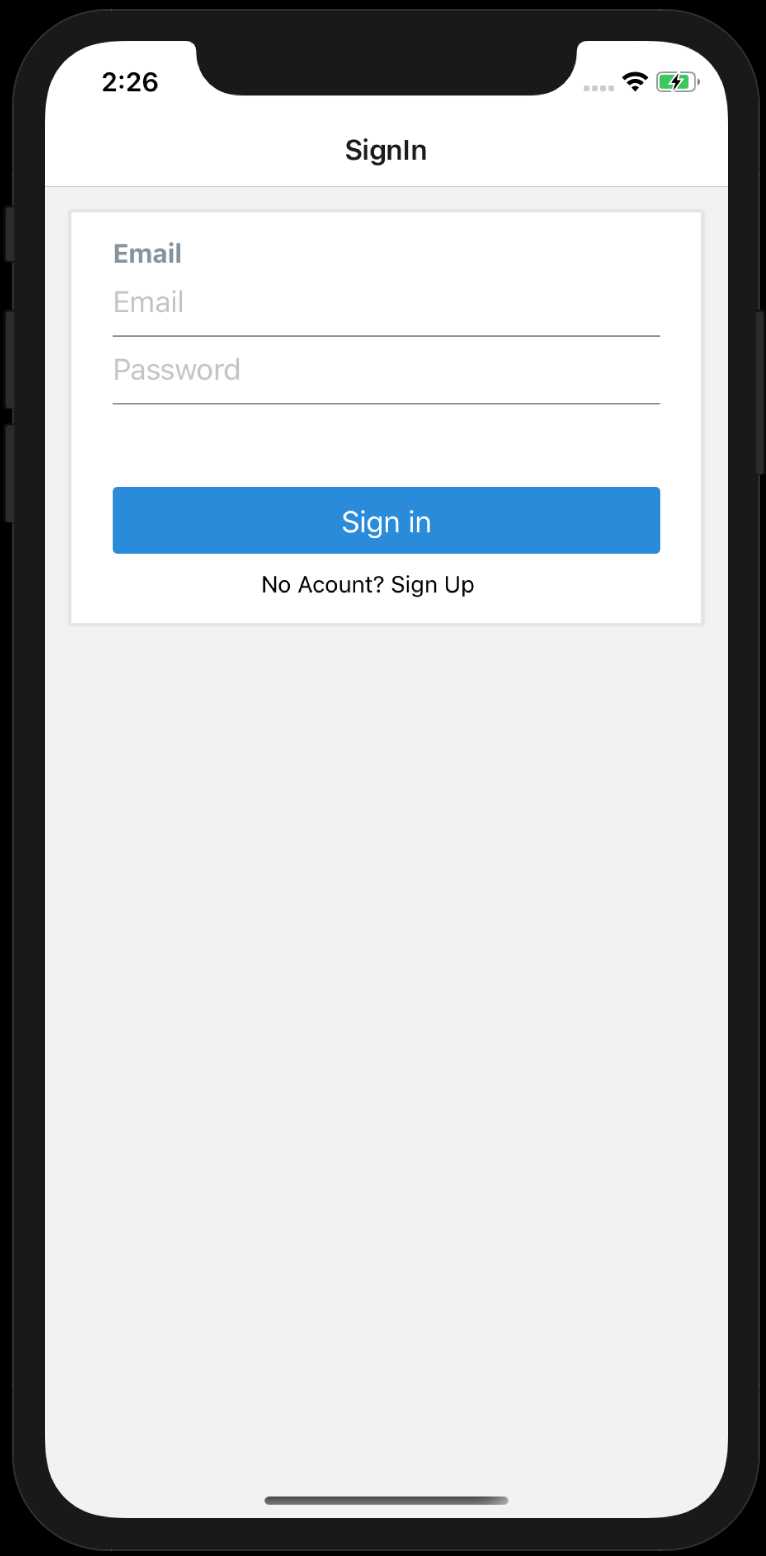
Here is the complete signInScreen.js,
import React, { useEffect, useState, useContext } from 'react';
import { validateAll } from 'indicative/validator';
import { View, Text } from 'react-native';
import {
Input,
Card,
FormValidationMessage,
Button
} from 'react-native-elements';
import { AuthContext } from '../../../utils/authContext';
const SignInScreen = ({ navigation }) => {
const [emailAddress, setemailAddress] = useState('');
const [password, setPassword] = useState('');
const [SignUpErrors, setSignUpErrors] = useState({});
const { signIn, signUp } = useContext(AuthContext);
const handleSignIn = () => {
// https://indicative.adonisjs.com
const rules = {
email: 'required|email',
password: 'required|string|min:6|max:40'
};
const data = {
email: emailAddress,
password: password
};
const messages = {
required: field => ${field} is required,
'username.alpha': 'Username contains unallowed characters',
'email.email': 'Please enter a valid email address',
'password.min': 'Wrong Password?'
};
validateAll(data, rules, messages)
.then(() => {
console.log('success sign in');
signIn({ emailAddress, password });
})
.catch(err => {
const formatError = {};
err.forEach(err => {
formatError[err.field] = err.message;
});
setSignUpErrors(formatError);
});
};
return (
<View>
<Card>
<Input
label={'Email'}
placeholder="Email"
value={emailAddress}
onChangeText={setemailAddress}
errorStyle={{ color: 'red' }}
errorMessage={SignUpErrors ? SignUpErrors.email : null}
/>
<Input
placeholder="Password"
value={password}
onChangeText={setPassword}
secureTextEntry
errorStyle={{ color: 'red' }}
errorMessage={SignUpErrors ? SignUpErrors.password : null}
/>
<Button
buttonStyle={{ margin: 10, marginTop: 50 }}
title="Sign in"
onPress={() => handleSignIn()}
/>
<Text style={{ marginLeft: 100 }} onPress={() => signUp()}>
No Acount? Sign Up
</Text>
</Card>
</View>
);
};
export default SignInScreen;Now with our screens complete we can build our main application to navigate between the screens.
App.js
App.js will leverage some react hook features.
createContext: shares data between components without us needed to pass it down.
const AuthContext = createContext({});useEffect: fetches the token from storage or presents the signUp screen if none is found.
useEffect(() => {
// Fetch the token from storage then navigate to our appropriate place
const bootstrapAsync = async () => {
let userToken;
try {
userToken = await AsyncStorage.getItem('userToken');
} catch (e) {
// Restoring token failed
}
dispatch({ type: 'RESTORE_TOKEN', token: userToken });
};
bootstrapAsync();
}, []);useMemo: used to memorize our context functions to avoid calling them on every render. UseMemo will only recompute when one of the inputs has changed.
const authContextValue = useMemo(
() => ({
signIn: async data => {
if (
data &&
data.emailAddress !== undefined &&
data.password !== undefined
) {
dispatch({ type: 'SIGN_IN', token: 'Token-For-Now' });
} else {
dispatch({ type: 'TO_SIGNIN_PAGE' });
}
},
signOut: async data => {
dispatch({ type: 'SIGN_OUT' });
},
signUp: async data => {
if (
data &&
data.emailAddress !== undefined &&
data.password !== undefined
) {
dispatch({ type: 'SIGNED_UP', token: 'dummy-auth-token' });
} else {
dispatch({ type: 'TO_SIGNUP_PAGE' });
}
}
}),
[]
);useReducer: handles our complex state logic, setting flags that determine which screen to display.
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(
(prevState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'TO_SIGNUP_PAGE':
return {
...prevState,
isLoading: false,
isSignedUp: false,
noAccount: true
};
case 'TO_SIGNIN_PAGE':
return {
...prevState,
isLoading: false,
isSignedIn: false,
noAccount: false
};
case 'RESTORE_TOKEN':
return {
...prevState,
userToken: action.token,
isLoading: false
};
case 'SIGNED_UP':
return {
...prevState,
isSignedIn: true,
isSignedUp: true,
isLoading: false,
userToken: action.token
};
case 'SIGN_IN':
return {
...prevState,
isSignedOut: false,
isSignedIn: true,
isSignedUp: true,
userToken: action.token
};
case 'SIGN_OUT':
return {
...prevState,
isSignedOut: true,
isSignedIn: false,
isSignedUp: true,
userToken: null
};
}
},
{
isLoading: true,
isSignedOut: false,
isSignedUp: false,
noAccount: false,
isSignedIn: false,
userToken: null
}
);Using Navigator
Now we can call the react-navigator to build our screens
In your app.js import the navigators and initialize them
import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native';
import { createStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/stack';
import { createDrawerNavigator, DrawerItems } from '@react-navigation/drawer';
const Stack = createStackNavigator();
const Drawer = createDrawerNavigator();Home Stack
The homepage will build a stack that has a side drawer component.
Our home screen navigation stack will look like this:
const createHomeStack = () => {
const { signOut } = useContext(AuthContext);
return (
<Stack.Navigator>
<Stack.Screen
name="Home Screen"
component={createDrawer}
initialParams={{ singOut: signOut }}
/>
</Stack.Navigator>
);
};Here is our side drawer navigator:
const createDrawer = () => {
const { signOut } = useContext(AuthContext);
return (
<Drawer.Navigator>
<Drawer.Screen
name="Home Screen"
component={HomeScreen}
initialParams={{
id: 111,
SignOutButton: () => (
<Button
title="Sign Me out"
onPress={signOut}
color={styles.signOutBtn.color}
/>
)
}}
/>
<Drawer.Screen name="Screen1" component={Screen1} />
<Drawer.Screen name="Screen2" component={Screen2} />
</Drawer.Navigator>
);
};You will need to build the screen components (HomeScreen, Screen1, Screen2, SplashScreen) and import them into your app.js
Here is a basic example of a screen:
import React from 'react';
import { View, Text } from 'react-native';
const aScreen = () => {
return (
<View style={styles.center}>
<Text style={styles.title}>Screen2 </Text>
</View>
);
};
export default aScreen;To render our Navigators in App.js we need to wrap our screens in a NavigationContainer but to also handle our data sharing we will need to wrap everything inside our AuthContext provider.
return (
<AuthContext.Provider value={authContextValue}>
<NavigationContainer>
<Stack.Navigator>{chooseScreen(state)}</Stack.Navigator>
</NavigationContainer>
</AuthContext.Provider>
);The two helper functions were created to help us dictate which screen gets rendered in our authorization flow.
stateConditionString(): returns a single value, telling our switch case which Stack Screen to return. If you look at our useReducer, when the useContext is called from one of our pages it will dispatch the action and update state. The state flags is how we determine which page to naviagte to.
export const stateConditionString = state => {
let navigateTo = '';
if (state.isLoading) {
navigateTo = 'LOAD_APP';
}
if (state.isSignedIn && state.userToken && state.isSignedUp) {
navigateTo = 'LOAD_HOME';
}
if (!state.isSignedUp && state.noAccount) {
navigateTo = 'LOAD_SIGNUP';
}
if (!state.isSignedIn && !state.noAccount) {
navigateTo = 'LOAD_SIGNIN';
}
return navigateTo;
};chooseScreen(): When we define screens like this, React Navigation will only see the valid screen. This makes it impossible to navigate to the HomeScreen when the user is not signed in.
const chooseScreen = state => {
let navigateTo = stateConditionString(state);
let arr = [];
switch (navigateTo) {
case 'LOAD_APP':
arr.push(<Stack.Screen name="Splash" component={SplashScreen} />);
break;
case 'LOAD_SIGNUP':
arr.push(
<Stack.Screen
name="SignUp"
component={SignUpScreen}
options={{
title: 'Sign Up',
// When logging out, a pop animation feels intuitive
animationTypeForReplace: state.isSignout
? 'pop'
: 'push'
}}
/>
);
break;
case 'LOAD_SIGNIN':
arr.push(<Stack.Screen name="SignIn" component={SignInScreen} />);
break;
case 'LOAD_HOME':
arr.push(
<Stack.Screen
name="Home"
component={createHomeStack}
options={{
title: 'Home Screen Parent',
headerStyle: { backgroundColor: 'black' },
headerTintColor: 'white'
}}
/>
);
break;
default:
arr.push(<Stack.Screen name="SignIn" component={SignInScreen} />);
break;
}
return arr[0];
};At this point we have everything we need to build our authentication flow. I’d like to point out that we are not using a real token. In a production app, we need to send the data to server and get a token. You’ll also need to handle errors if sign in failed.

Wrap Up 🎉
Building an authentication flow with react navigation 5.0 is straight to the point with the power of react hooks. We can define different screens based on conditions and use the react navigations stack history manager to help us guard against un authorized page access.
I also encourage you to checkout Indicative, it has some powerful features to help validate and sanitize your data.
I hope this guide has helped you understand how authorization screens can be created in react-native using the lastest features of react and react-navigation. I’d enjoy hearing about your experience in the comments below.
What do you think, does this guide need a How-To video?
Feel free to reach out if you’d like some help.